By: Christina and Zachary

Oxygen call be written as: O2.
The most important element on earth is oxygen. Without it, human life simply could not exist. Humans can live for weeks without water, and go without food for months, but without oxygen, life could only carry on for a little while.
The respiratory system is the system of the body that deals with breathing. When we breathe, the body takes in the oxygen that it needs and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesn't need.
Every minute of every day you breathe in air. Without it you could live only a few minutes. The air that you breathe is oxygen. Oxygen is the most important part of the air. All animals and plants need it, too.
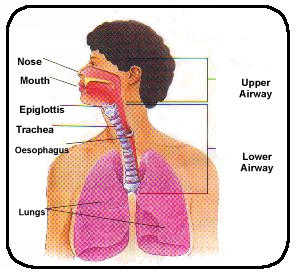
First the body breathes in the air which is sucked through the nose or mouth and down through the trachea (windpipe). The trachea is a pipe shaped by rings of cartilage. It divides into two tubes called bronchi. These carry air into each lung.
Your blood carries oxygen to all the cells of your body. Every cell needs oxygen to stay alive.
The diaphragm is the muscle that controls the breathing process. As the diaphragm flattens it causes the chest to expand and air is sucked into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, the chest collapses and the air in the lungs is forced out.
Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli. The walls are so thin and close to each other that the air easily seeps through. In this way, oxygen seeps through into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide, in the bloodstream, seeps through into the alveoli, and is then removed from the body when we breathe out.
On the tops of high mountains, there is not enough oxygen to keep a man alive.
Here is an experiment for you to do at home that shows air dissolved in water:
Fill a glass with water.
Cover the glass, so the air from outside doesn't get into the water.
After two or three hours you can see bubbles of air, air that was dissolved in the water. Part of the air in the bubbles is oxygen.
Click here to see how the body works.